Install NetBird
If you're a new user you should visit the Quickstart Guide. This will help you setup your management dashboard and connect your first client. For quick install instructions, including desktop applications, visit the install prompt through the management dashboard. To view all the client installation methods we've set up a variety of platform specific pages.
The NetBird client (agent) allows a peer to join a pre-existing NetBird deployment. If a NetBird deployment is not yet available, there are both managed and self-hosted options available.
Install and Update Instructions
Additional Platforms
- Install on Synology
- Install on TrueNAS
- Install on pfSense
- Install on OPNSense
- Install on Raspberry Pi
- Install on Proxmox VE
Running NetBird with SSO Login
Desktop UI Application
If you installed the Desktop UI client, you can launch it and click on Connect.
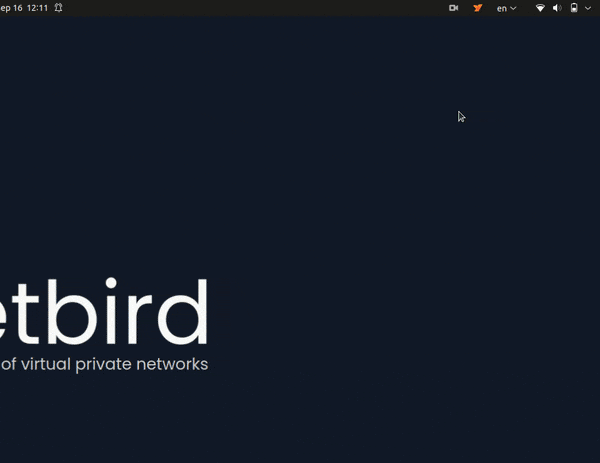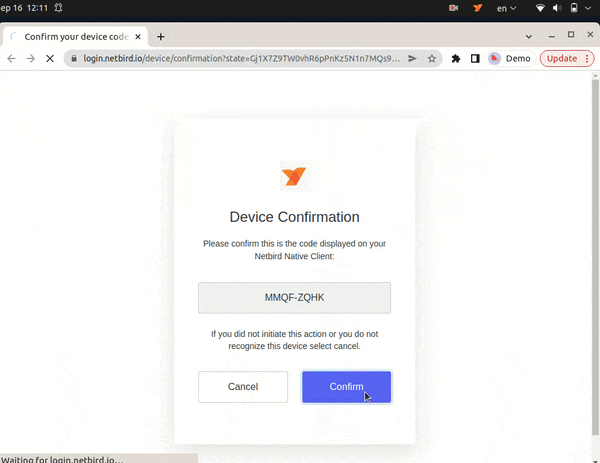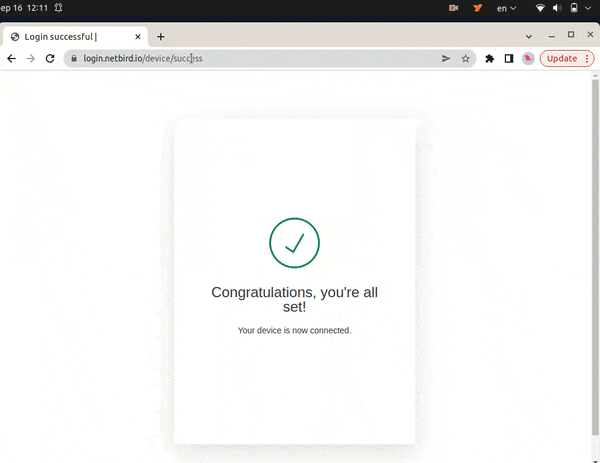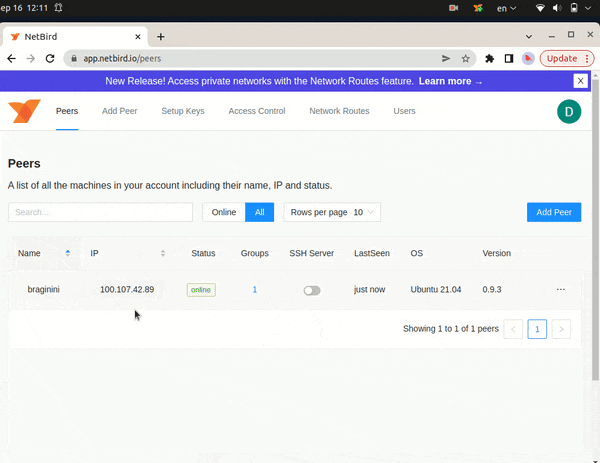
It will open your browser, and you will be prompt for email and password. Follow the instructions.
CLI
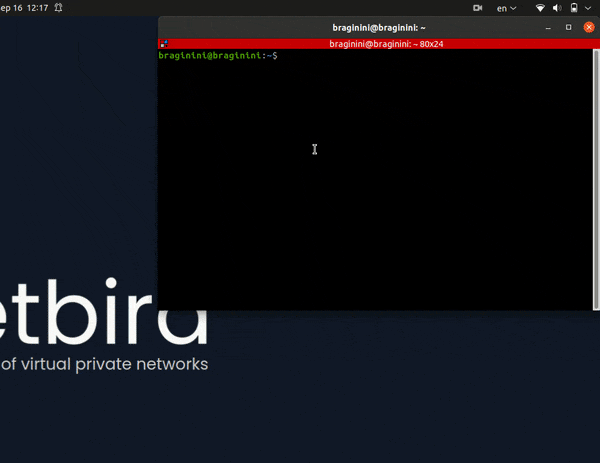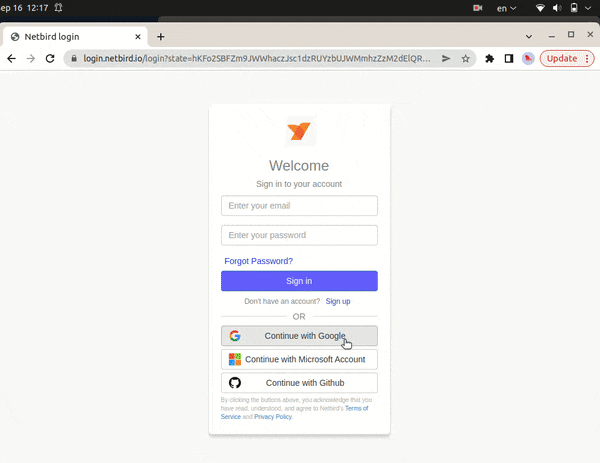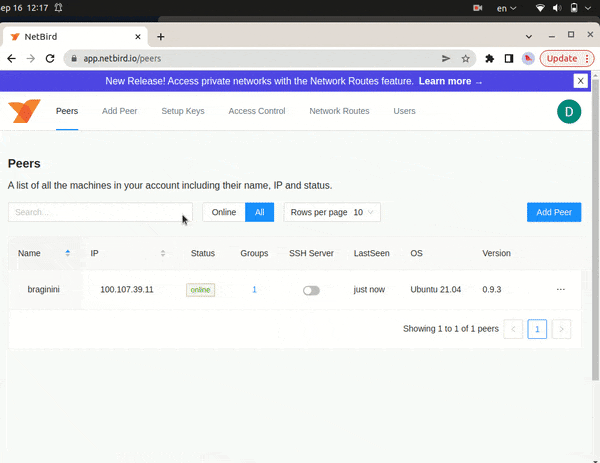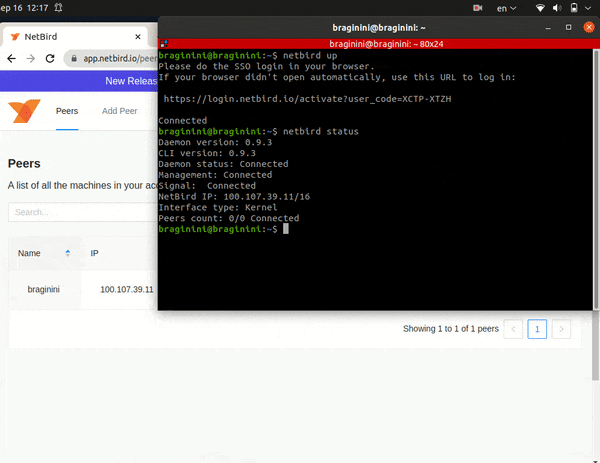
Alternatively, you could use command line. Simply run
netbird up
It will open your browser, and you will be prompt for email and password. Follow the instructions.
Check connection status:
netbird status
Running NetBird with a Setup Key
In case you are activating a server peer, you can use a setup key as described in the steps below.
This is especially helpful when you are running multiple server instances with infrastructure-as-code tools like ansible and terraform.
- Login to the Management Service. You need to have a
setup keyin hand (see setup keys).
For all systems:
netbird up --setup-key <SETUP KEY>
For Docker, you can run with the following command:
docker run --network host --privileged --rm -d -e NB_SETUP_KEY=<SETUP KEY> -v netbird-client:/var/lib/netbird netbirdio/netbird:<TAG>
TAG > 0.6.0 version
Alternatively, if you are hosting your own Management Service provide --management-url property pointing to your Management Service:
netbird up --setup-key <SETUP KEY> --management-url http://localhost:33073
You could also omit the
--setup-keyproperty. In this case, the tool will prompt for the key.
- Check connection status:
netbird status
- Check your IP:
On macOS :
sudo ifconfig utun100
On Linux:
ip addr show wt0
On Windows:
netsh interface ip show config name="wt0"

