NetBird Agent command line interface (CLI)
The NetBird client installation adds a binary called netbird to your system. This binary runs as a daemon service to connect
your computer or server to the NetBirt network as a peer. But it can also be used as a client to control the daemon service.
This section will explore the commands available in netbird.
Syntax
Use the following syntax to run netbird commands from your terminal window:
netbird [command] [subcommand] [flags]
command: Specifies the operation that you want to perform or a top-level command:up,login,down,status,ssh,version, andservicesubcommand: Specifies the operation to be executed for a top-level command likeservice:install,uninstall,start, andstopflags: Specifies optional flags. For example, you can use the--setup-keyflag to specify the setup key to be used in the commandsloginandup
To see detailed command information, use the flag --help after each command
Configuration precedence
This is the CLI configuration precedence (highest to lowest priority):
- environment variables (eg:
NB_WIREGUARD_PORT) - command line flags (eg:
--wireguard-port) - configuration file entries
<profile>.json(formerly:config.json), eg:WgPortkey
We are preserving the unusual priority of environment variables for backwards compatibility with existing deployments.
Global flags
netbird has a set of global flags that are available in every command. They specify settings that are core or shared between two or more commands, e.g. --setup-key is used by login and up to authenticate the client against a management service.
Below is the list of global flags:
--admin-url string Admin Panel URL [http|https]://[host]:[port] (default "https://app.netbird.io")
-A, --anonymize anonymize IP addresses and non-netbird.io domains in logs and status output
--daemon-addr string Daemon service address to serve CLI requests [unix|tcp]://[path|host:port] (default "unix:///var/run/netbird.sock")
--log-file string sets NetBird log path. If console is specified the the log will be output to stdout (default "/var/log/netbird/client.log")
-l, --log-level string sets NetBird log level (default "info")
-m, --management-url string Management Service URL [http|https]://[host]:[port] (default "https://api.netbird.io:443")
-p, --preshared-key string Sets Wireguard PreSharedKey property. If set, then only peers that have the same key can communicate.
-k, --setup-key string Setup key obtained from the Management Service Dashboard (used to register peer)
Environment Variables
Every flag of a netbird command can be passed as an environment variable. We are using the following rule for the environment variables composition:
PREFIX_FLAGNAMEand for flags with multiple parts:PREFIX_FLAGNAMEPART1_FLAGNAMEPART2- The prefix is always NB
- The flag parts are separated by a dash ("-") when passing as flags and with an underscore ("_") when passing as an environment variable
For example, let's check how we can pass --config and --management-url as environment variables:
export NB_CONFIG="/opt/netbird/config.json"
export NB_MANAGEMENT_URL="https://api.self-hosted.com:443"
netbird up
The up command would process the variables, read the configuration file on /opt/netbird/config.json and attempt to connect to the management service running at https://api.self-hosted.com:443.
Here are some additional examples of environment variables:
# Disable profiles feature
export NB_DISABLE_PROFILES=true
# Disable update settings functionality
export NB_DISABLE_UPDATE_SETTINGS=true
# Set custom log level
export NB_LOG_LEVEL=debug
# Set custom daemon address
export NB_DAEMON_ADDR="tcp://localhost:8080"
Commands
up
Single command to log in and start the NetBird client. It can send a signal to the daemon service or run in the foreground with the flag --foreground-mode.
The command will check if the peer is logged in and connect to the management service. If the peer is not logged in, by default, it will attempt to initiate an SSO login flow.
Flags
--allow-server-ssh Allow SSH server on peer. If enabled, the SSH server will be permitted
--disable-auto-connect Disables auto-connect feature. If enabled, then the client won't connect automatically when the service starts.
--disable-ssh-auth Disable SSH JWT authentication. If enabled, any peer with network access can connect without user authentication
--dns-resolver-address string Sets a custom address for NetBird's local DNS resolver. If set, the agent won't attempt to discover the best ip and port to listen on. An empty string "" clears the previous configuration. E.g. --dns-resolver-address 127.0.0.1:5053 or --dns-resolver-address ""
--ssh-jwt-cache-ttl int SSH JWT token cache TTL in seconds. Set to 0 to disable caching (default). E.g. --ssh-jwt-cache-ttl 3600 for 1-hour cache
--enable-rosenpass [Experimental] Enable Rosenpass feature. If enabled, the connection will be post-quantum secured via Rosenpass.
--enable-ssh-local-port-forwarding Enable local port forwarding on SSH server. Requires --allow-server-ssh
--enable-ssh-remote-port-forwarding Enable remote port forwarding on SSH server. Requires --allow-server-ssh
--enable-ssh-root Enable root user login on SSH server. Requires --allow-server-ssh
--enable-ssh-sftp Enable SFTP subsystem on SSH server. Requires --allow-server-ssh
--external-ip-map strings Sets external IPs maps between local addresses and interfaces.You can specify a comma-separated list with a single IP and IP/IP or IP/Interface Name. An empty string "" clears the previous configuration. E.g. --external-ip-map 12.34.56.78/10.0.0.1 or --external-ip-map 12.34.56.200,12.34.56.78/10.0.0.1,12.34.56.80/eth1 or --external-ip-map ""
--extra-dns-labels strings Sets DNS labels. You can specify a comma-separated list of up to 32 labels. An empty string "" clears the previous configuration. E.g. --extra-dns-labels vpc1 or --extra-dns-labels vpc1,mgmt1 or --extra-dns-labels ""
-F, --foreground-mode start service in foreground
-h, --help help for up
--interface-name string Wireguard interface name (default "utun100")
--rosenpass-permissive [Experimental] Enable Rosenpass in permissive mode to allow this peer to accept WireGuard connections without requiring Rosenpass functionality from peers that do not have Rosenpass enabled.
--wireguard-port uint16 Wireguard interface listening port (default 51820)
Usage
The minimal form of running the command is:
netbird up
If you are running on a self-hosted environment, you can pass your management url by running the following:
netbird up --management-url https://api.self-hosted.com:443
if you want to run in the foreground, you can use "console" as the value for --log-file and run the command with sudo:
sudo netbird up --log-file console
On Windows, you may need to run the command from an elevated terminal session.
In case you need to use a setup key, use the --setup-key flag :
netbird up --setup-key AAAA-BBB-CCC-DDDDDD
You can set extra DNS labels with the --extra-dns-labels flag:
netbird up --setup-key AAAA-BBB-CCC-DDDDDD --extra-dns-labels vpc1,mgmt1
This feature requires a setup-key with permissions to add peers with the extra labels.
Multiple peers with the same extra labels will generate grouped DNS labels on the client side, and this feature can be used for DNS round-robing load balancing.
login
Command to authenticate the NetBird client to a management service. If the peer is not logged in, by default, it will attempt to initiate an SSO login flow.
Usage
The minimal form of running the command is:
netbird login
If you are running on a self-hosted environment, you can pass your management url by running the following:
netbird login --management-url https://api.self-hosted.com:443
In case you need to use a setup key, use the --setup-key flag:
netbird login --setup-key AAAA-BBB-CCC-DDDDDD
Passing a management url and a setup key:
netbird login --setup-key AAAA-BBB-CCC-DDDDDD --management-url https://api.self-hosted.com:443
down
Command to stop a connection with the management service and other peers in a NetBird network. After running this command, the daemon service will enter an Idle state.
Usage
The minimal form of running the command is:
netbird down
status
Retrieves the peer status from the daemon service.
Flags
-d, --detail display detailed status information in human-readable format
--filter-by-ips strings filters the detailed output by a list of one or more IPs, e.g., --filter-by-ips 100.64.0.100,100.64.0.200
--filter-by-names strings filters the detailed output by a list of one or more peer FQDN or hostnames, e.g., --filter-by-names peer-a,peer-b.netbird.cloud
--filter-by-status string filters the detailed output by connection status(connected|disconnected), e.g., --filter-by-status connected
-A, --anonymize anonymize IP addresses and non-netbird.io domains in the status output
-h, --help help for status
--ipv4 display only NetBird IPv4 of this peer, e.g., --ipv4 will output 100.64.0.33
--json display detailed status information in json format
--yaml display detailed status information in yaml format
Usage
The minimal form of running the command is:
netbird status
This will output:
OS: linux/amd64
Daemon version: 0.27.4
CLI version: 0.27.4
Management: Connected
Signal: Connected
Relays: 2/2 Available
Nameservers: 1/1 Available
NetBird IP: 100.119.62.6/16
Interface type: Kernel
Quantum resistance: false
Routes: -
Peers count: 2/3 Connected
If you want to see more details about the peer connections, you can use the --detail or -d flag:
netbird status -d
This will output:
Peers detail:
Peer:
NetBird IP: 100.119.85.4
Public key: 2lI3F+fDUWh58g5oRN+y7lPHpNcEVWhiDv/wr1/jiF8=
Status: Disconnected
-- detail --
Connection type: -
Direct: false
ICE candidate (Local/Remote): -/-
ICE candidate endpoints (Local/Remote): -/-
Last connection update: 26 seconds ago
Last Wireguard handshake: -
Transfer status (received/sent) 0 B/0 B
Quantum resistance: false
Routes: -
Latency: 10.74ms
Peer:
NetBird IP: 100.119.201.225
Public key: +jkH8cs/Fo83qdB6dWG16+kAQmGTKYoBYSAdLtSOV10=
Status: Connected
-- detail --
Connection type: P2P
Direct: true
ICE candidate (Local/Remote): host/host
ICE candidate endpoints (Local/Remote): -/-
Last connection update: 26 seconds ago
Last Wireguard handshake: 25 seconds ago
Transfer status (received/sent) 2.0 KiB/355 B
Quantum resistance: false
Routes: 10.0.0.0/24
Latency: 20.14ms
Peer:
NetBird IP: 100.119.230.104
Public key: R7olj0S8jiYMLfOWK+wDto+j3pE4vR54tLGrEQKgBSw=
Status: Connected
-- detail --
Connection type: P2P
Direct: true
ICE candidate (Local/Remote): host/host
ICE candidate endpoints (Local/Remote): -/-
Last connection update: 26 seconds ago
Last Wireguard handshake: 24 seconds ago
Transfer status (received/sent) 2.4 MiB/532 KiB
Quantum resistance: false
Routes: -
Latency: 16.24ms
OS: linux/amd64
Daemon version: 0.27.4
CLI version: 0.27.4
Management: Connected to https://api.netbird.io:443
Signal: Connected to https://signal.netbird.io:443
Relays:
[stun:stun.netbird.io:5555] is Available
[turns:turn.netbird.io:443?transport=tcp] is Available
Nameservers:
[8.8.8.8:53, 8.8.4.4:53] for [.] is Available
NetBird IP: 100.119.62.6/16
Interface type: Kernel
Quantum resistance: false
Routes: -
Peers count: 2/3 Connected
To filter the peers' output by connection status, you can use the --filter-by-status flag with either "connected" or "disconnected" as value:
netbird status -d --filter-by-status connected
This will output:
Peers detail:
Peer:
NetBird IP: 100.119.201.225
Public key: +jkH8cs/Fo83qdB6dWG16+kAQmGTKYoBYSAdLtSOV10=
Status: Connected
-- detail --
Connection type: P2P
Direct: true
ICE candidate (Local/Remote): host/host
ICE candidate endpoints (Local/Remote): -/-
Last connection update: 28 seconds ago
Last Wireguard handshake: 27 seconds ago
Transfer status (received/sent) 2.0 KiB/355 B
Quantum resistance: false
Routes: 10.0.0.0/24
Latency: 20.14ms
Peer:
NetBird IP: 100.119.230.104
Public key: R7olj0S8jiYMLfOWK+wDto+j3pE4vR54tLGrEQKgBSw=
Status: Connected
-- detail --
Connection type: P2P
Direct: true
ICE candidate (Local/Remote): host/host
ICE candidate endpoints (Local/Remote): -/-
Last connection update: 28 seconds ago
Last Wireguard handshake: 26 seconds ago
Transfer status (received/sent) 2.4 MiB/532 KiB
Quantum resistance: false
Routes: -
Latency: 16.24ms
OS: linux/amd64
Daemon version: 0.27.4
CLI version: 0.27.4
Management: Connected to https://api.netbird.io:443
Signal: Connected to https://signal.netbird.io:443
Relays:
[stun:stun.netbird.io:5555] is Available
[turns:turn.netbird.io:443?transport=tcp] is Available
Nameservers:
[8.8.8.8:53, 8.8.4.4:53] for [.] is Available
NetBird IP: 100.119.62.6/16
Interface type: Kernel
Quantum resistance: false
Routes: -
Peers count: 2/3 Connected
To filter the peers' output by peer IP addresses, you can use the --filter-by-ips flag with one or more IPs separated by a comma as a value:
netbird status -d --filter-by-ips 100.119.201.225
This will output:
Peers detail:
Peer:
NetBird IP: 100.119.201.225
Public key: +jkH8cs/Fo83qdB6dWG16+kAQmGTKYoBYSAdLtSOV10=
Status: Connected
-- detail --
Connection type: P2P
Direct: true
ICE candidate (Local/Remote): host/host
ICE candidate endpoints (Local/Remote): -/-
Last connection update: 32 seconds ago
Last Wireguard handshake: 30 seconds ago
Transfer status (received/sent) 2.0 KiB/355 B
Quantum resistance: false
Routes: 10.0.0.0/24
Latency: 20.14ms
OS: linux/amd64
Daemon version: 0.27.4
CLI version: 0.27.4
Management: Connected to https://api.netbird.io:443
Signal: Connected to https://signal.netbird.io:443
Relays:
[stun:stun.netbird.io:5555] is Available
[turns:turn.netbird.io:443?transport=tcp] is Available
Nameservers:
[8.8.8.8:53, 8.8.4.4:53] for [.] is Available
NetBird IP: 100.119.62.6/16
Interface type: Kernel
Quantum resistance: false
Routes: -
Peers count: 2/3 Connected
You can combine both filters and get the peers that are both connected and with specific IPs:
netbird status -d --filter-by-status connected --filter-by-ips 100.119.85.4,100.119.230.104
This will output:
Peers detail:
Peer:
NetBird IP: 100.119.230.104
Public key: R7olj0S8jiYMLfOWK+wDto+j3pE4vR54tLGrEQKgBSw=
Status: Connected
-- detail --
Connection type: P2P
Direct: true
ICE candidate (Local/Remote): host/host
ICE candidate endpoints (Local/Remote): -/-
Last connection update: 35 seconds ago
Last Wireguard handshake: 33 seconds ago
Transfer status (received/sent) 2.4 MiB/532 KiB
Quantum resistance: false
Routes: -
Latency: 16.24ms
OS: linux/amd64
Daemon version: 0.27.4
CLI version: 0.27.4
Management: Connected to https://api.netbird.io:443
Signal: Connected to https://signal.netbird.io:443
Relays:
[stun:stun.netbird.io:5555] is Available
[turns:turn.netbird.io:443?transport=tcp] is Available
Nameservers:
[8.8.8.8:53, 8.8.4.4:53] for [.] is Available
NetBird IP: 100.119.62.6/16
Interface type: Kernel
Quantum resistance: false
Routes: -
Peers count: 2/3 Connected
The peer with IP 100.119.85.4 wasn't returned because it was not connected
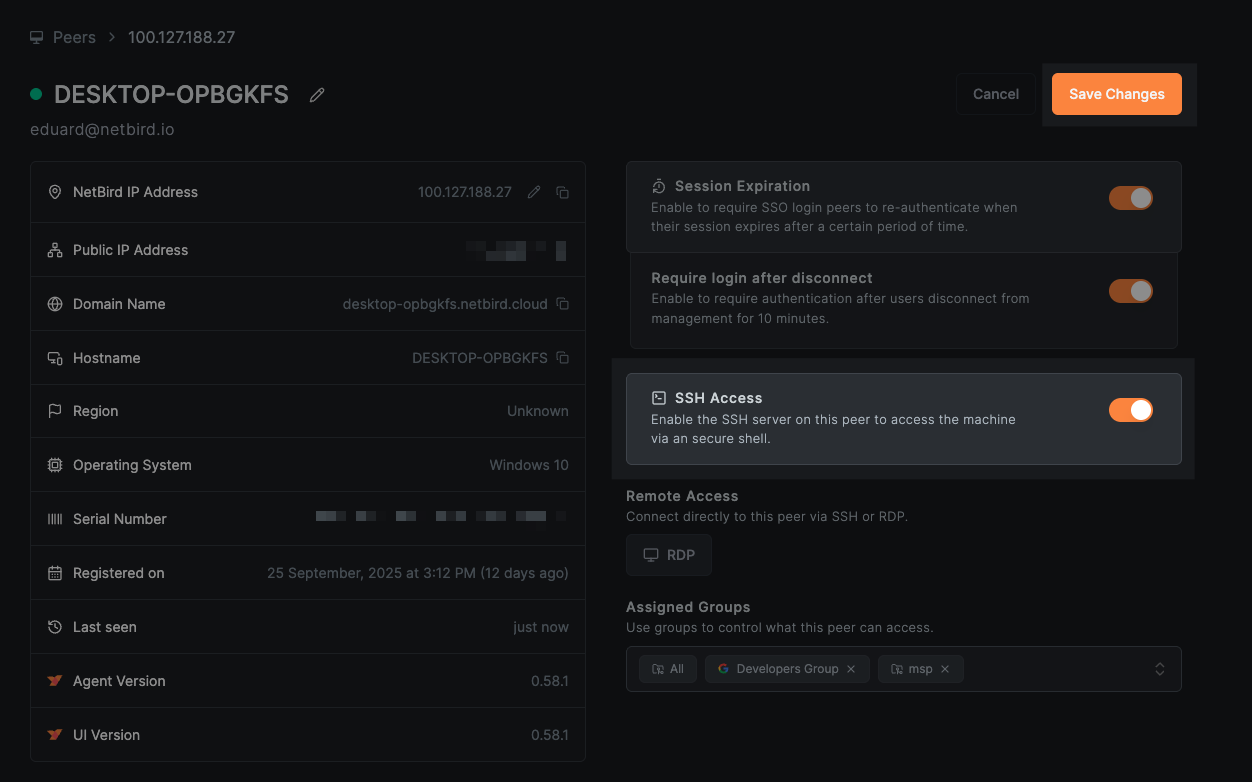
ssh
Command to connect via SSH to a remote peer in your NetBird network. The ssh command has several subcommands for different operations.
Before using this command, make sure that SSH Access is enabled both on the target peer and in the NetBird Dashboard. Learn more about enabling SSH access.
ssh (connect)
Connect to a remote peer via SSH with an interactive shell or execute a command.
Flags:
-L, --local-forward string Local port forwarding (e.g., 8080:localhost:80)
-R, --remote-forward string Remote port forwarding (e.g., 8080:localhost:3000)
-p, --port int Remote SSH port (default: 22)
Arguments:
user@host: The remote user and NetBird peer IP address[command]: Optional command to execute on the remote peer
Usage:
Interactive shell:
netbird ssh user@100.119.230.104
Execute a single command:
netbird ssh user@100.119.230.104 "uptime"
Local port forwarding (forward local port 8080 to remote port 80):
netbird ssh -L 8080:localhost:80 user@100.119.230.104
Remote port forwarding (forward remote port 8080 to local port 3000):
netbird ssh -R 8080:localhost:3000 user@100.119.230.104
Port forwarding must be enabled on the SSH server using --enable-ssh-local-port-forwarding and/or --enable-ssh-remote-port-forwarding flags.
For SFTP and SCP, use native clients (sftp and scp commands) which work with NetBird SSH automatically.
Troubleshooting
Connection fails:
- Ensure SSH is enabled on the target peer:
netbird up --allow-server-ssh - Verify SSH Access is enabled in the dashboard (Peers > your_peer > SSH Access)
- Check that an ACL policy allows TCP port 22022
Authentication fails:
- Complete the OIDC flow when prompted (browser window will open)
- Verify your IdP is properly configured
- To disable JWT authentication:
netbird up --allow-server-ssh --disable-ssh-auth
Port forwarding not working:
- Ensure the server has the appropriate flags:
netbird up --allow-server-ssh \ --enable-ssh-local-port-forwarding \ --enable-ssh-remote-port-forwarding
version
Outputs the netbird command version.
Usage
The minimal form of running the command is:
netbird version
This will output:
0.8.2
service
The service command is a top-level command with subcommands to perform operations related to the daemon service.
You should run the service command with elevated permissions.
service install
The install installs the daemon service on the system.
Usage
The minimal form of running the command is:
sudo netbird service install
You can use the global flags to configure the daemon service. For instance, you can set a debug log level with the flag --log-level
sudo netbird service install --log-level debug
You can set a custom configuration path with the flag --config
sudo netbird service install --config /opt/netbird/config.json
Service-specific flags
--disable-profiles Disables profiles feature. If enabled, the client will not be able to change or edit any profile. To persist this setting, use: netbird service install --disable-profiles
--disable-update-settings Disables update settings feature. If enabled, the client will not be able to change or edit any settings. To persist this setting, use: netbird service install --disable-update-settings
The --disable-profiles flag can also be set using the NB_DISABLE_PROFILES environment variable. Set it to any value (e.g., true, 1, yes) to enable this feature.
The --disable-update-settings flag can also be set using the NB_DISABLE_UPDATE_SETTINGS environment variable. Set it to any value (e.g., true, 1, yes) to enable this feature.
service uninstall
The uninstall uninstalls the daemon service from the system.
Usage
The minimal form of running the command is:
sudo netbird service uninstall
service start
Starts the daemon service
Usage
The minimal form of running the command is:
sudo netbird service start
If you installed the service with --disable-profiles or --disable-update-settings, these settings will persist and the respective features will remain disabled when the service starts.
service stop
Stops the daemon service
Usage
The minimal form of running the command is:
sudo netbird service stop
service restart
Restarts the daemon service
Usage
The minimal form of running the command is:
sudo netbird service restart
service status
Shows the status of the daemon service
Usage
The minimal form of running the command is:
sudo netbird service status
service reconfigure
Reconfigures the daemon service with current settings
Usage
The minimal form of running the command is:
sudo netbird service reconfigure
If you installed the service with --disable-profiles or --disable-update-settings, these settings will persist and the respective features will remain disabled after reconfiguration.
debug
The debug command provides tools for diagnosing and understanding the internal operations of the NetBird daemon.
Usage
To access debugging options:
netbird debug [command]
Subcommands
bundle: Create a debug bundle that includes logs and system information for troubleshooting.for: Run the daemon with trace logging for a specified duration and create a debug bundle.log: Manage logging levels for the NetBird daemon.
Flags
-h, --help help for debug
debug bundle
Generates a compressed archive containing diagnostic information, which can be used for troubleshooting. The file will be generated in the a temporary directory and the path will be printed to the console. The file is only accessible as root/Administrator.
Usage
To create a debug bundle:
netbird debug bundle [-A] [-S]
Examples
Create a debug bundle:
netbird debug bundle
This will output:
/tmp/netbird.debug.676945815.zip
Flags
-h, --help help for bundle
-A, --anonymize anonymize IP addresses and non-netbird.io domains in the debug output
-S, --system-info Adds system information to the debug bundle
debug for
Sets the logging level to trace, runs for the specified duration, and then generates a debug bundle. This is useful for capturing detailed logs over a period where issues are occurring.
Usage
To run debugging for a specific time period:
netbird debug for <time> [-A] [-S]
Examples
Run debugging for 5 minutes and generate an anonymized debug bundle:
netbird debug for 5m
This will output something similar to:
Netbird up
Log level set to trace.
Netbird down
Netbird up
Remaining time: 00:00:01
Duration completed
Creating debug bundle...
Netbird down
Log level restored to INFO
/tmp/netbird.debug.3162242909.zip
Flags
-h, --help help for for
-A, --anonymize anonymize IP addresses and non-netbird.io domains in the debug output
-S, --system-info Adds system information to the debug bundle
debug log
This subcommand manages the logging level for the NetBird daemon during the current session. The change in logging level is temporary and will revert back to the configured default upon daemon restart.
Usage
Adjust the logging level of the NetBird daemon:
netbird debug log level <level>
Available Levels
panic: for panic level, the highest level of severity.fatal: for fatal level errors that cause the program to exit.error: for error conditions.warn: for warning conditions.info: for informational messages.debug: for debug-level messages.trace: for trace-level messages, which include more fine-grained information than debug.
Examples
Set the logging level to debug:
netbird debug log level debug
This will output:
Log level set successfully to debug

