Remote Worker Access (VPN-to-Site)
This guide shows how to enable remote workers to securely access office resources using the Networks feature.
What You'll Achieve
After following this guide, employees will be able to access office servers, applications, and services while working remotely—without exposing those resources to the internet.
Remote Laptop ──────► NetBird Tunnel ──────► Routing Peer ──────► Office Server
(peer) (at office) (no NetBird)
Prerequisites
- A NetBird cloud account or self-hosted instance
- Admin access to office network infrastructure
- A server or VM at the office to serve as the routing peer
Step 1: Connect a Remote Worker Device to NetBird
If you haven't already, install NetBird on a remote worker's laptop and connect:
- Download NetBird from app.netbird.io/install
- Run the application and click Connect in the system tray
- Complete the sign-up process in your browser
- Verify the device appears in the NetBird dashboard under Peers
Step 2: Add the Remote Worker to a User Group
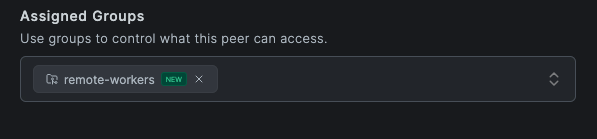
- In the Peers section of the dashboard, select the remote worker's device
- Under Assigned Groups, add a new group:
remote-workers
Step 3: Find Your Office Subnet
Before configuring NetBird, identify your office network's subnet.
On your routing peer device, run:
# Linux
ip route | grep -E "^[0-9]"
# Windows (PowerShell)
Get-NetRoute | Where-Object { $_.DestinationPrefix -like "*.*.*.*/*" }
Look for your local subnet, typically something like 10.0.0.0/24 or 192.168.1.0/24.
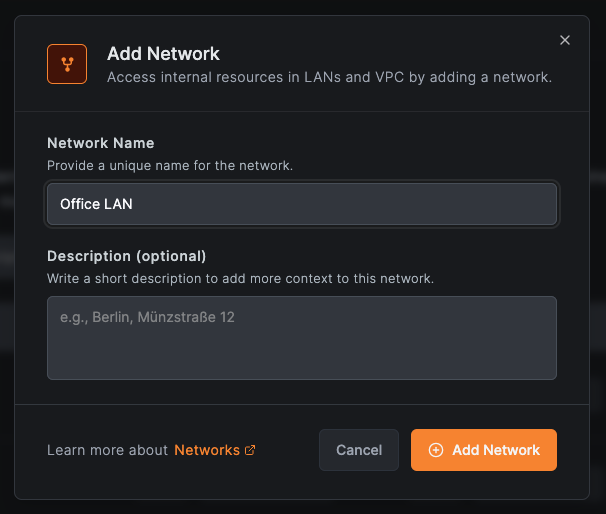
Step 4: Create a Network for Office Resources
- Go to Networks in the NetBird dashboard
- Click Add Network
- Name it "Office LAN" and click Save
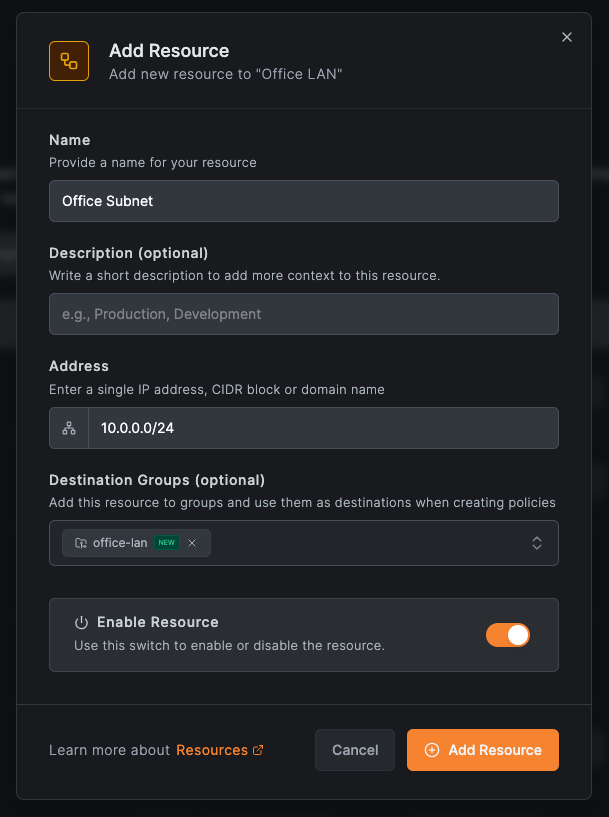
Step 5: Add Your Office Subnet as a Resource
- In your new network, click Add Resource
- Enter a name like "Office Subnet"
- Enter your office subnet (e.g.,
10.0.0.0/24) - Create a group called
office-lanfor the destination - Click Add Resource
For more granular access, add specific server IPs instead of the entire subnet. For example, add 10.0.0.50/32 to only allow access to a specific file server.
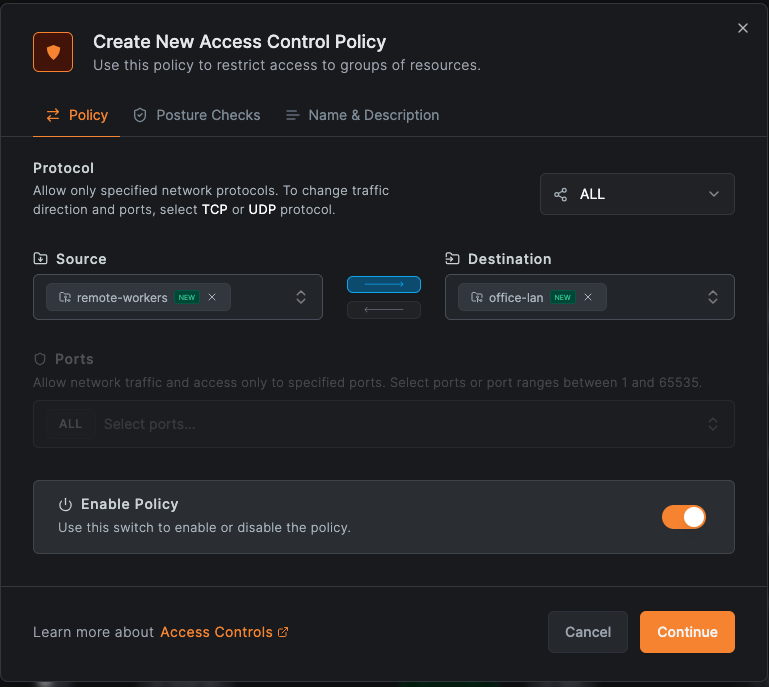
Step 6: Create an Access Policy
- After adding your resource, click Create Policy
- Set Source to "
remote-workers" - Set Destination to
office-lan - Set Protocol based on needs (TCP for most apps, All for full access)
- Name it "Remote Worker Office Access" and click Add Policy
Step 7: Set Up the Routing Peer
The routing peer forwards traffic from NetBird to your office network. Choose an always-on server at your office:
- A dedicated Linux VM
- A Windows Server
- A Docker container on an existing server
Install NetBird on your routing peer:
- In the NetBird dashboard, go to Setup Keys
- Create a new setup key (one-time use recommended). Add
office-lanto Auto-assigned groups and click Create Setup Key.
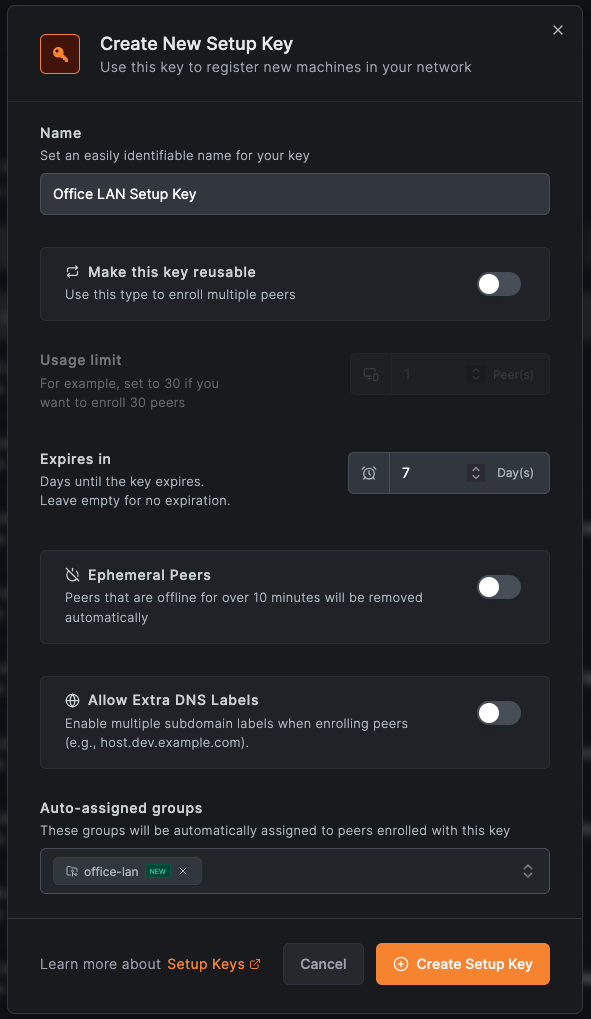
You can also add groups to peers manually after setup. Go to Peers, select the peer, and add groups under Assigned Groups.
- On your routing peer, run:
# Linux
curl -fsSL https://pkgs.netbird.io/install.sh | sh
sudo netbird up --setup-key YOUR_SETUP_KEY
# Windows (PowerShell as Administrator)
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "https://pkgs.netbird.io/install.ps1" -OutFile "install.ps1"; .\install.ps1
netbird up --setup-key YOUR_SETUP_KEY
- In the Networks view, click Add Routing Peer on your Office LAN network
- Select your new peer and click Add Routing Peer
Step 8: Test the Connection
From the remote worker's laptop (connected outside the office network):
ping 10.0.0.1 # Your office router
ping 10.0.0.50 # Your file server or other device
Remote workers can now access office resources from any location.
Step 9: Onboard Additional remote-workers
remote-workersFor additional remote workers:
- Have employees install NetBird from app.netbird.io/install
- After they connect, go to Peers and select their device
- Under Assigned Groups, add them to the "
remote-workers" group
Alternatively, create a setup key with "remote-workers" as an auto-assigned group for streamlined onboarding.
Best Practices for Business Deployments
Access Control
- Create specific groups for different access levels (e.g.,
it-admins,sales,engineering) - Use protocol restrictions (e.g., only allow RDP to certain servers)
- Implement time-limited setup keys for contractor access
High Availability
For critical connections, consider:
- Multiple routing peers at each location
- Monitoring routing peer health
- Automatic failover configuration
Security
- Enable Posture Checks to verify device compliance
- Use Activity Logging to audit access
- Implement MFA through your identity provider
Troubleshooting
Remote workers can't access office resources:
- Verify the routing peer is online and connected
- Check access policies include the user's group
- Ensure the routing peer can reach office resources locally
Slow performance:
- Check routing peer placement—it should have good network connectivity
- Consider enabling lazy connections for large deployments
- Review network route priorities if multiple routes exist
Next Steps
- Need Site-to-VPN or Site-to-Site? If office systems need to initiate connections to remote workers, or you need to connect branch offices, see Network Routes Use Cases
- Advanced configuration: See Advanced Configuration for masquerade options and detailed access control

